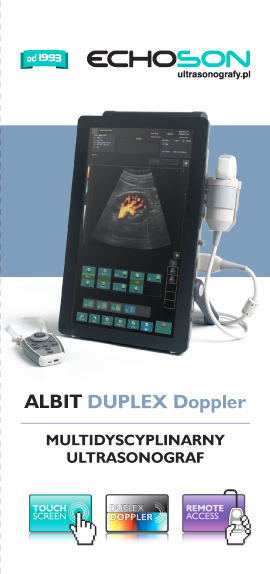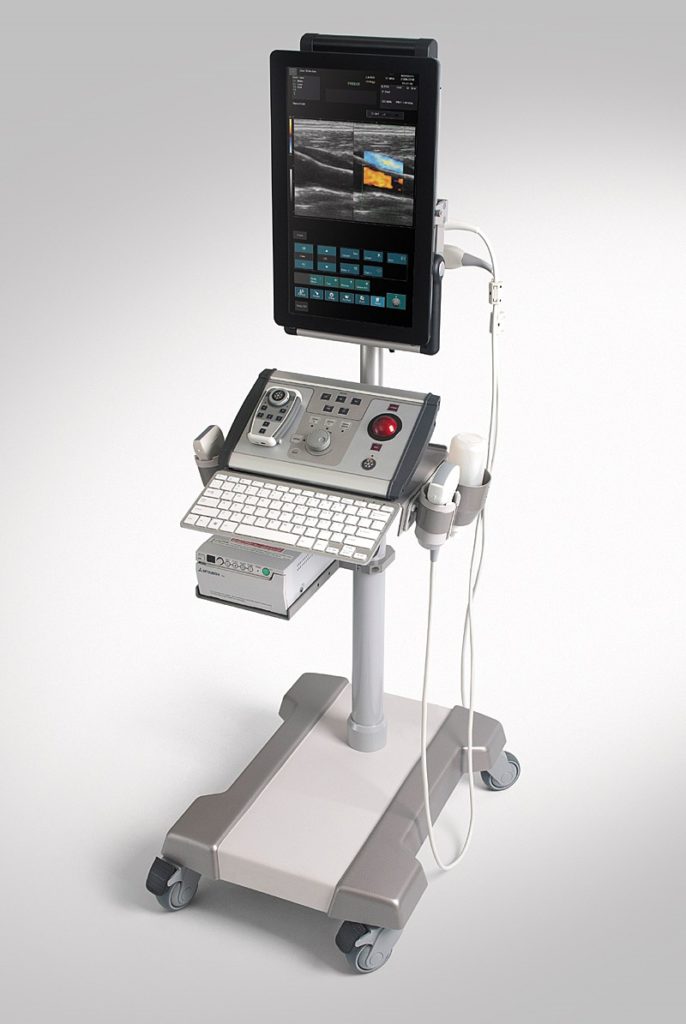


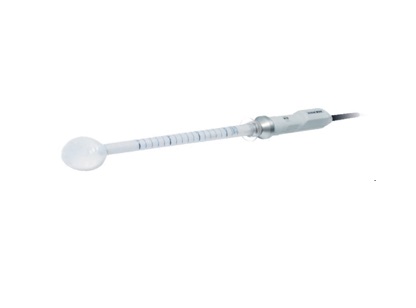
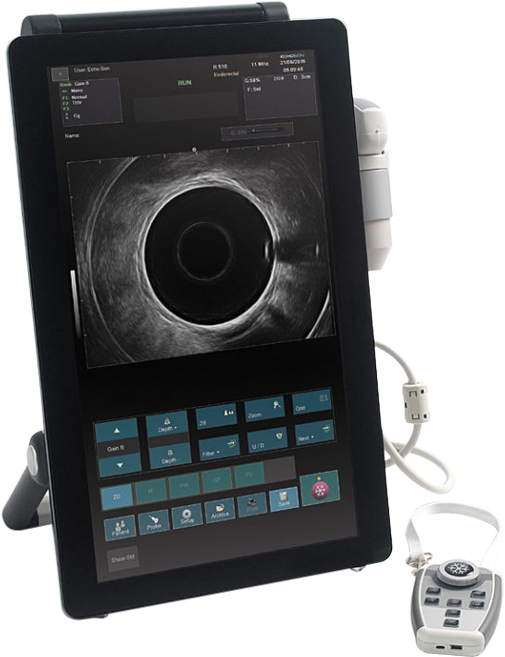
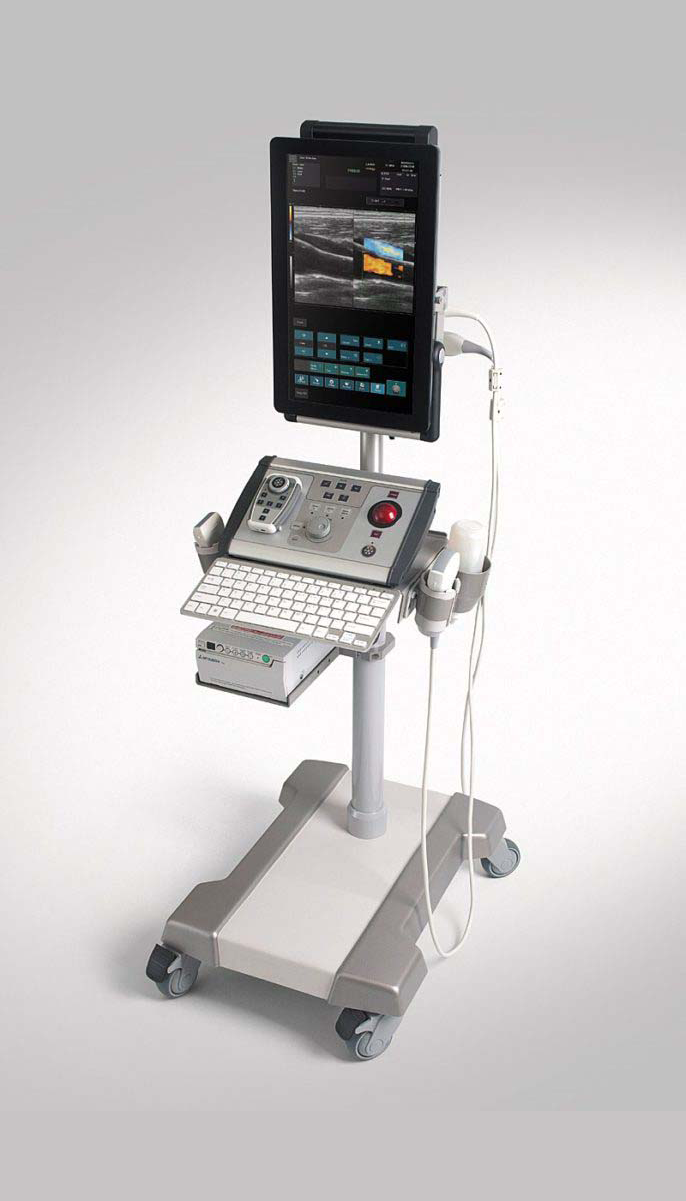
Albit was designed as a simple and effective ultrasound scanner for general imaging as well as specific applications, including monitoring of Endovascular treatments (sclerotherapy, EVLT, EVRF etc.), vascular diagnosis (deep vein thrombosis), Regional Anesthesia, Vascular Access (central and peripheral vascular implantation), Musculoskeletal, TRUS or Colorectal.
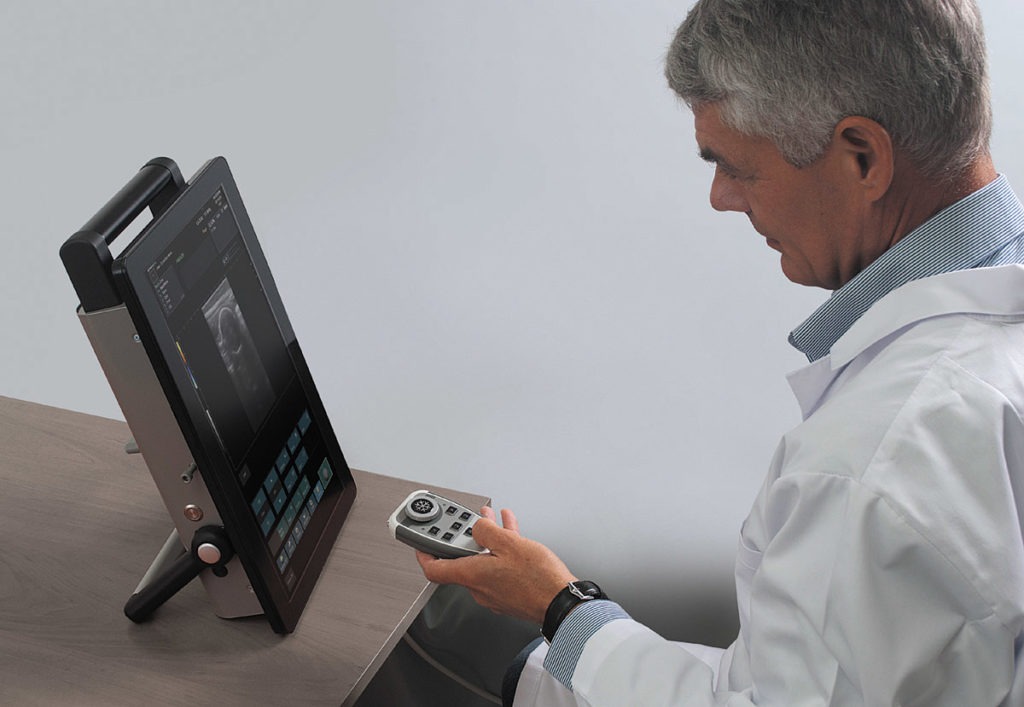
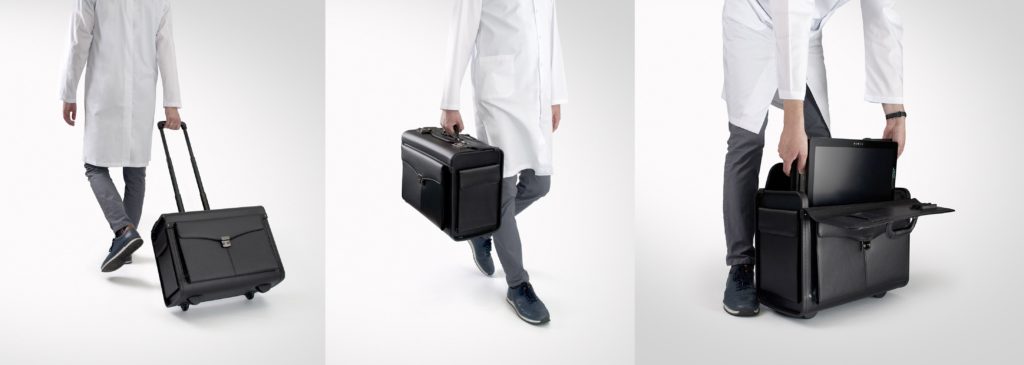
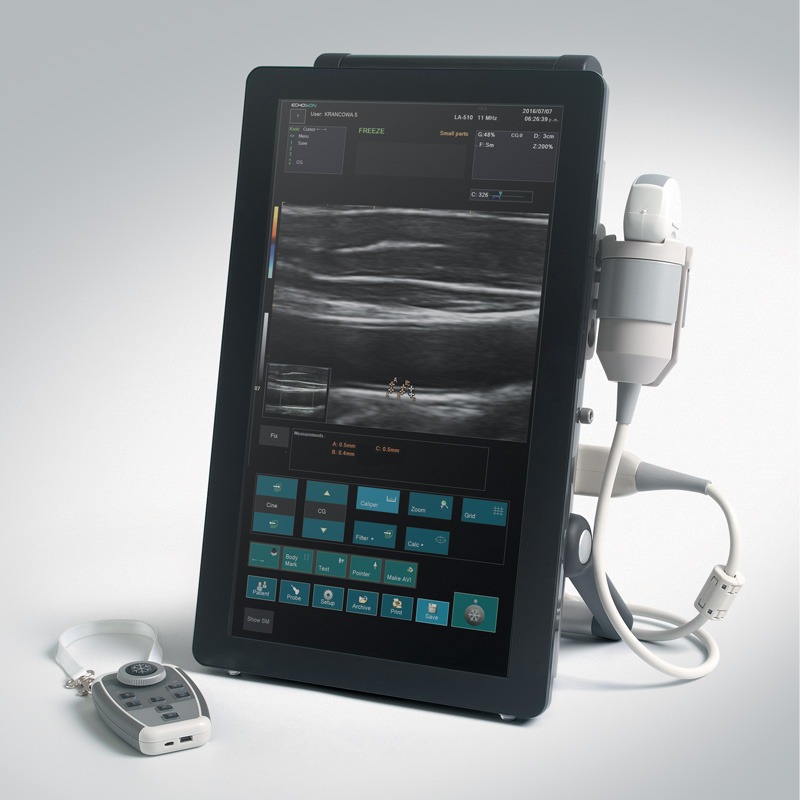
Albit interface based on touch-screen technology makes it friendly and very easy to use. Duplex Doppler (Color and Power Doppler Flow Maps) extends ultrasound diagnostics more efficiently and accurately, with maximum performance to price ratio. Unique and smart remote controller superbly improving working performance.
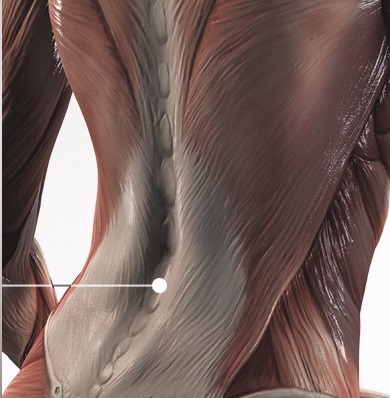
Endovascular Surgery
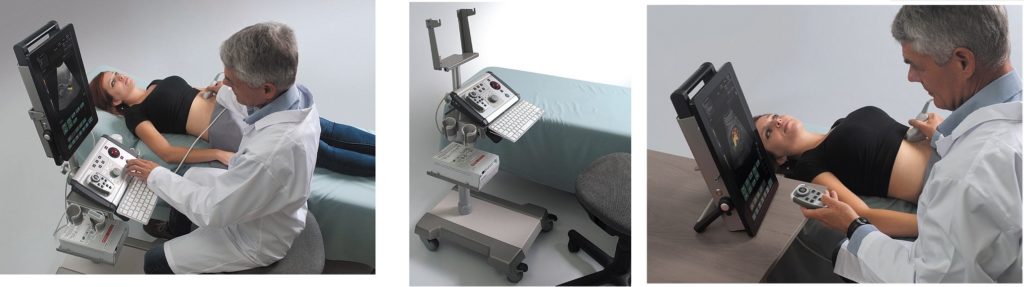
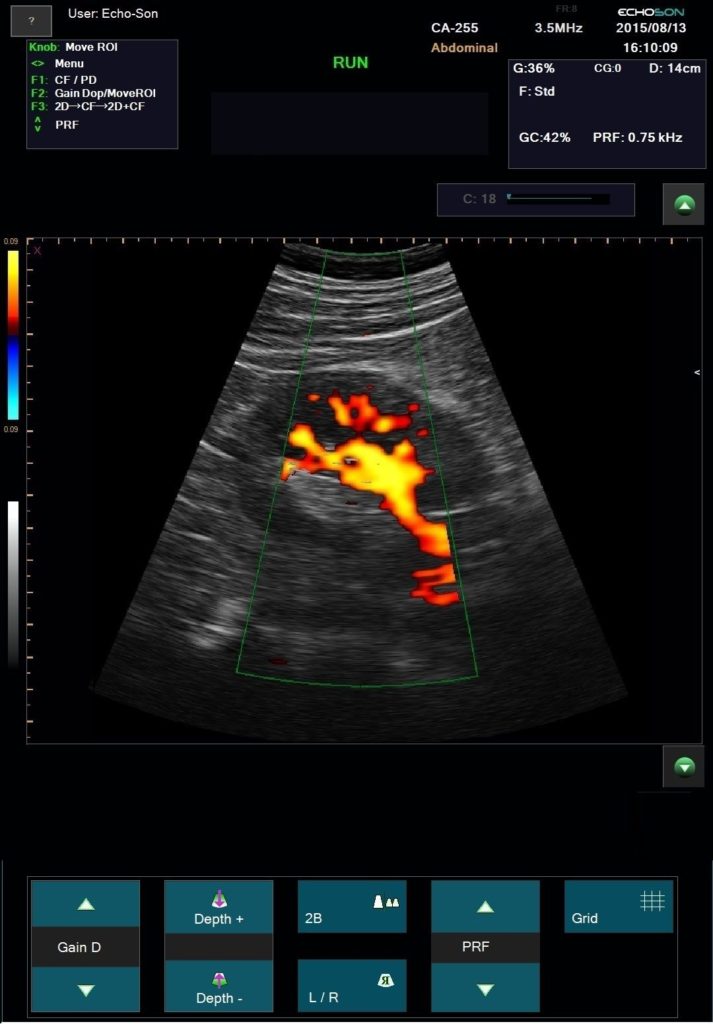
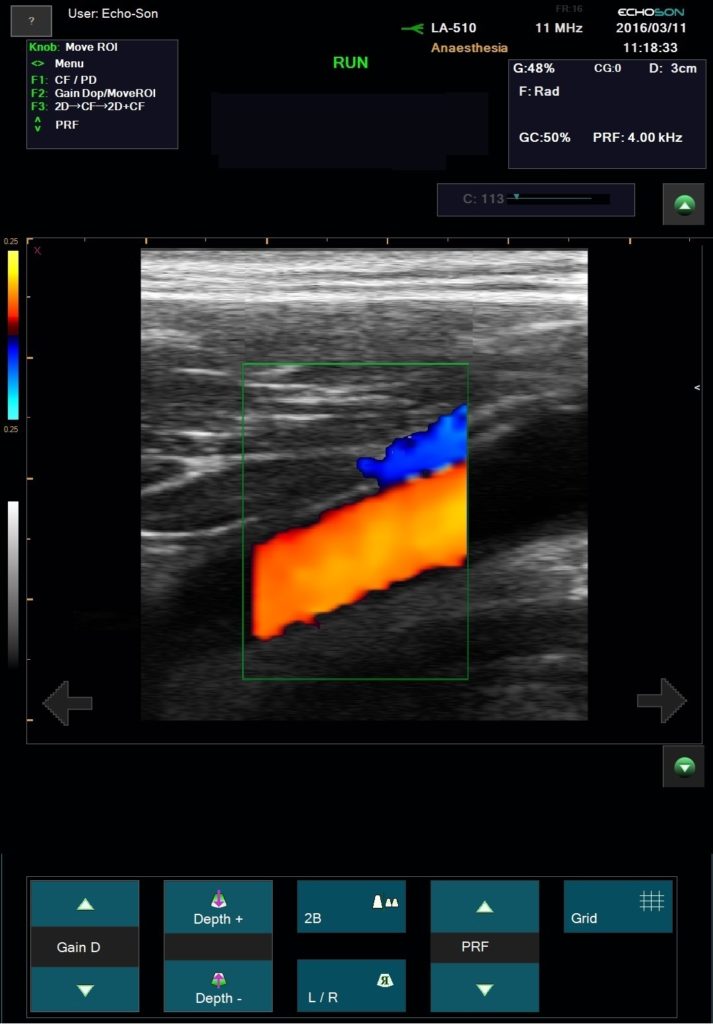
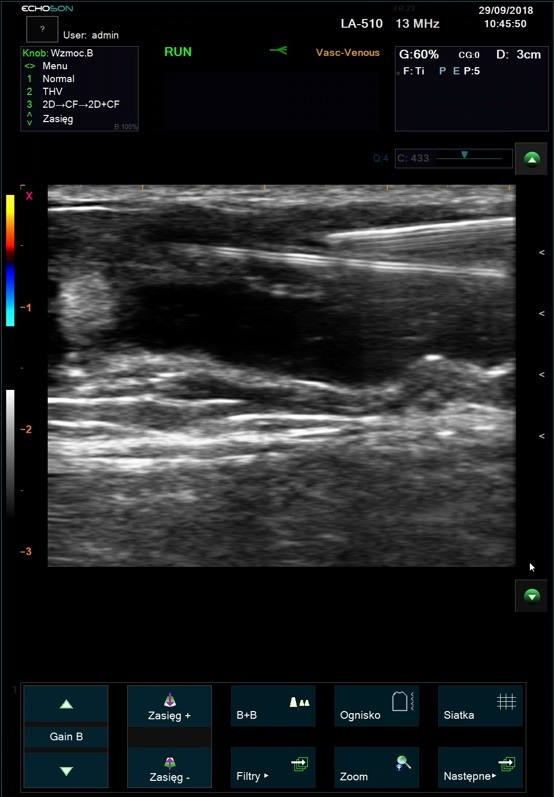
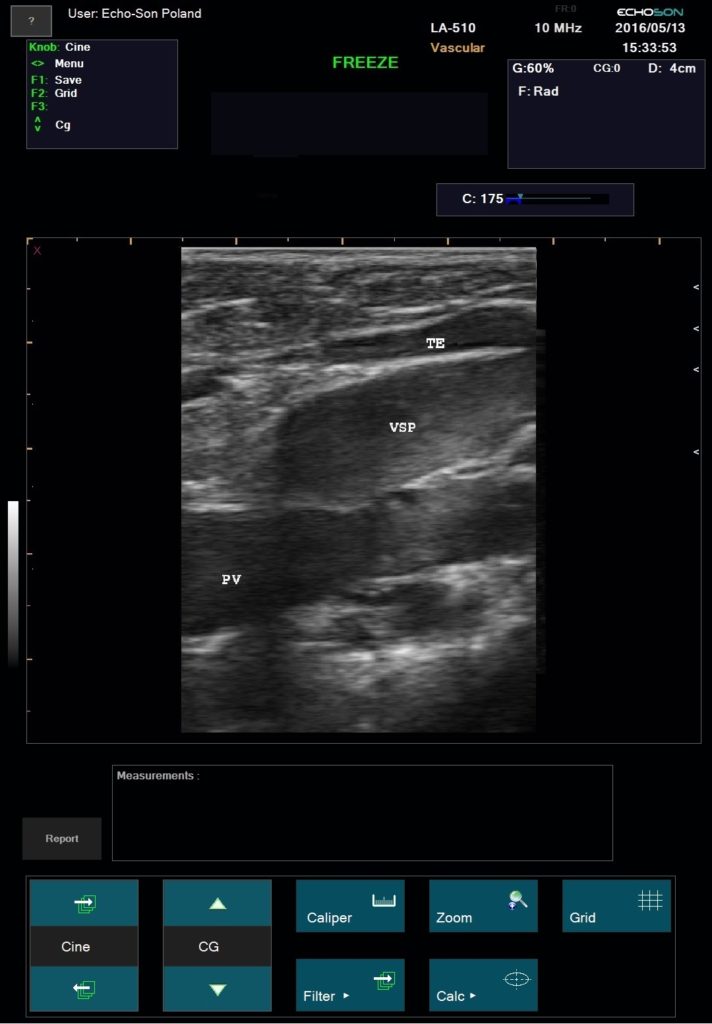
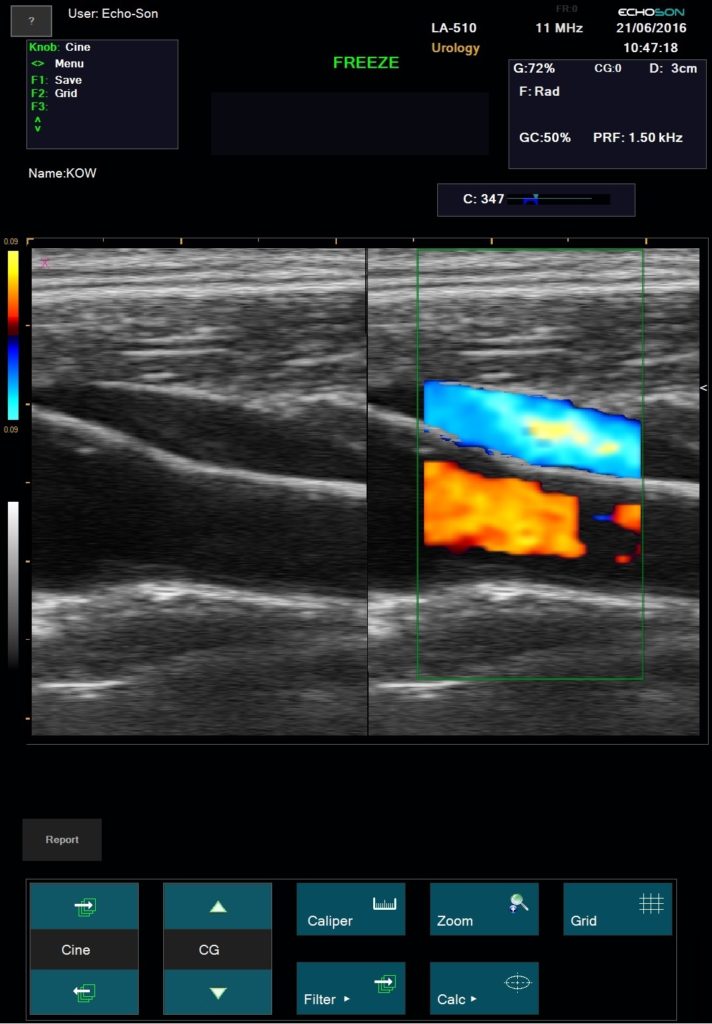
Duplex ultrasonography enables precise anatomical and hemodynamic diagnosis of recurrent varicose veins. This is a non invasive investigation which is the gold standard for investigating venous disease and is the most informative technique available.
ALBIT empower monitoring of the progress and process of endovascular treatments via ultrasound imaging of vessels, supported with Duplex Doppler (vessel mapping). Allows a localization and guiding of “tools” during angioplasty and revascularization as well as process and progress of sclerotherapy, EVLT, EVRF etc. treatments.
Excellent for all pre- and postoperative ultrasound investigation for peripheral vascular surgery.
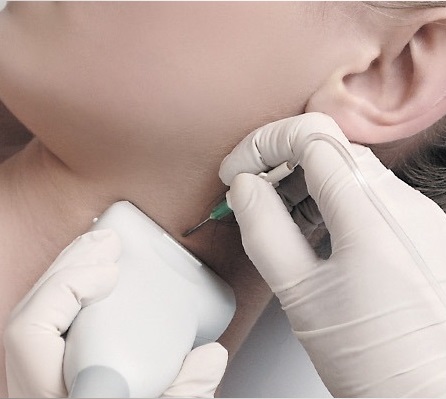
Regional Anesthesia & Vascular Access
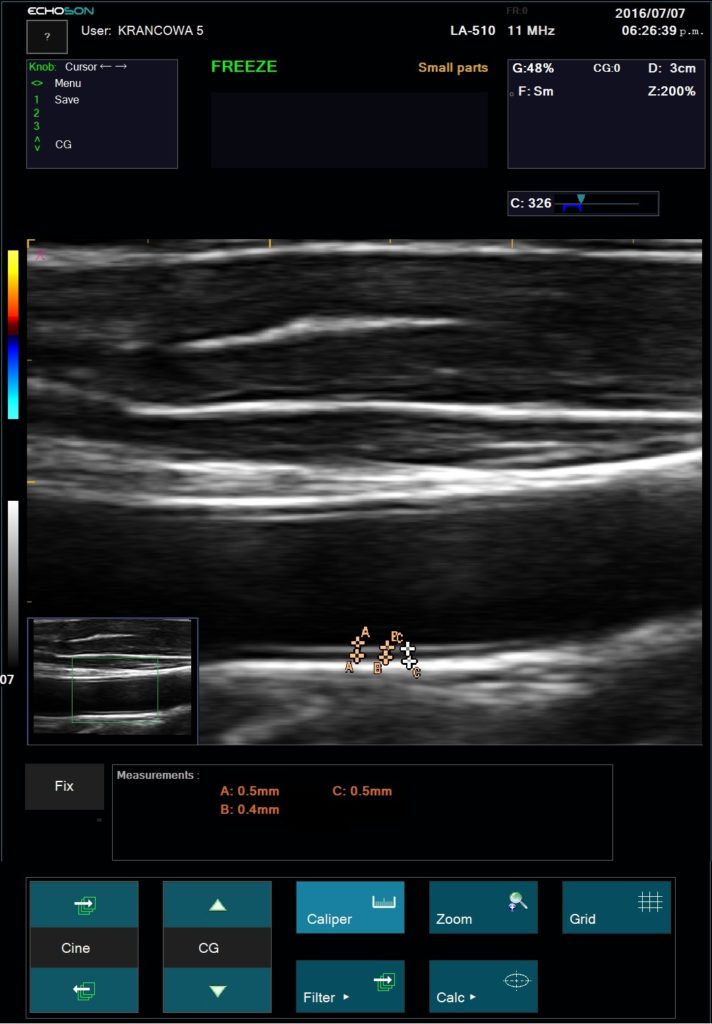
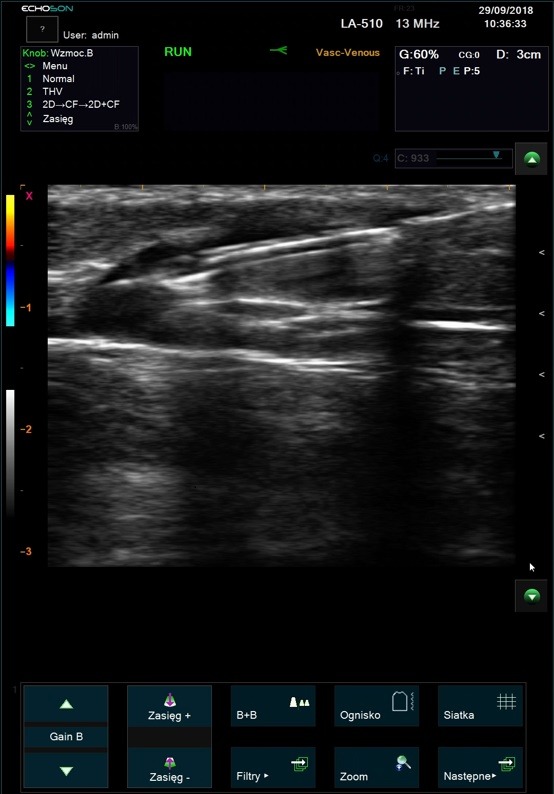
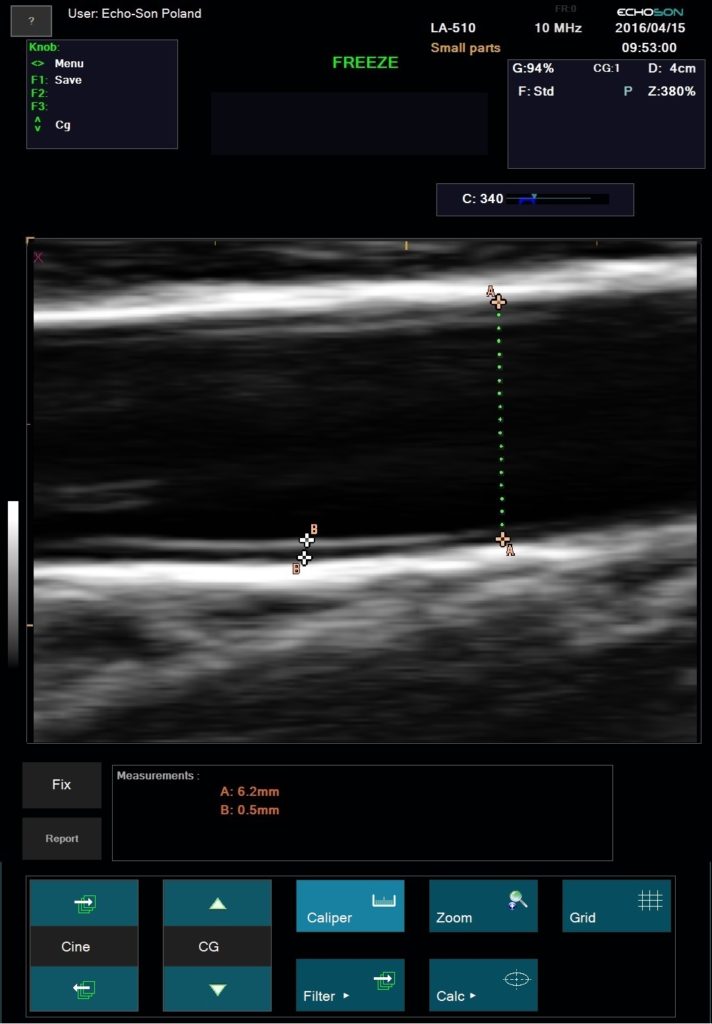
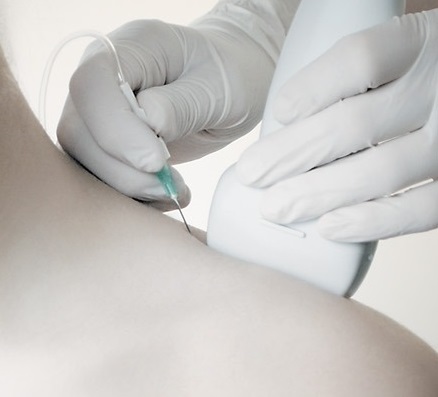
“Gold standard” technique for the direct visualization of nerves, adjacent structures and the position of the needle for local anesthetic blocks or drug delivery location.
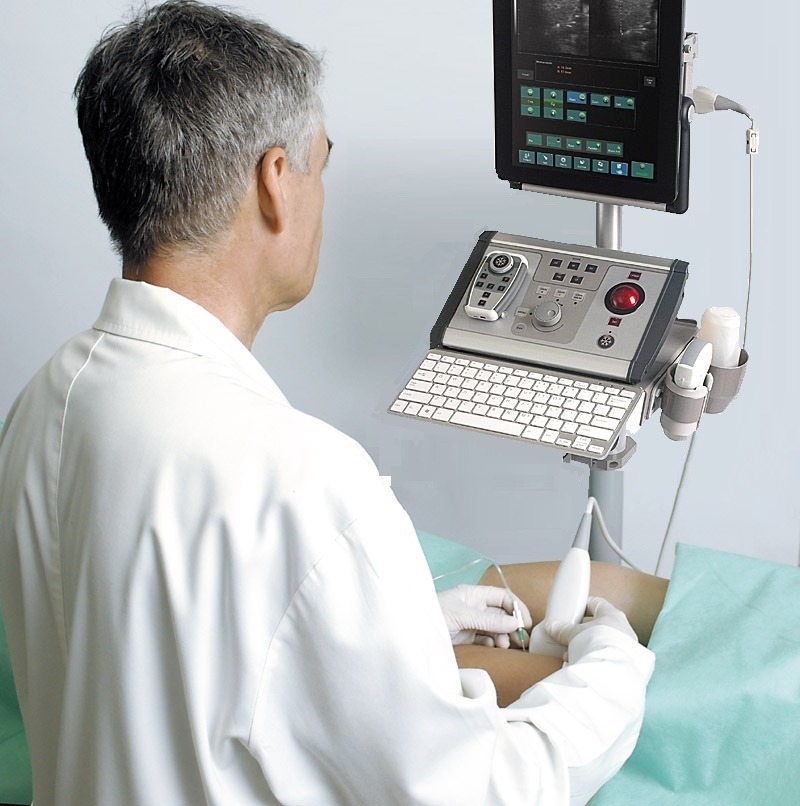
Empower rapid diagnostics and needle-guided procedures right at a patient’s bedside. Essential for Vascular Access procedures – central or peripheral venous catheters, dialysis catheters, oncologic ports.
Ultrasound imaging in anaesthetic practise strongly helps with cannulation of veins and arteries in adults and children. It is the main advantage and safety feature of this technique, that the targeted vessels and the surrounding anatomical structures are visualized and that the needle is advanced under continuous observation. Ultrasound imaging reduce the rate of unsuccessful cannulation attempts, which can be caused by anatomical variations or thrombi, occluding the targeted vessel.

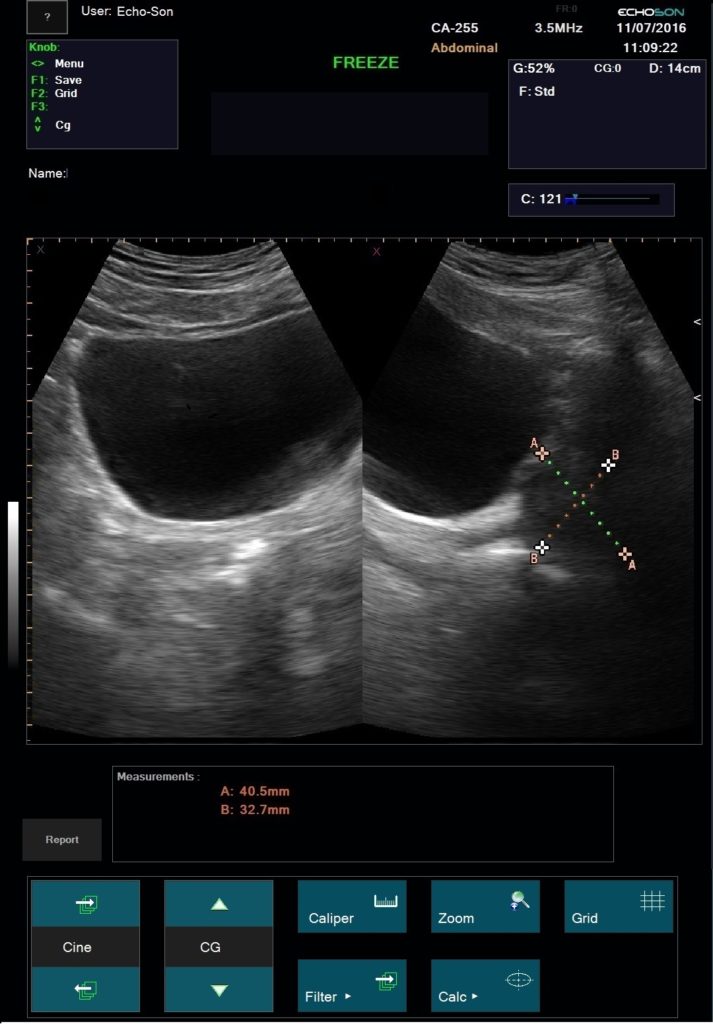
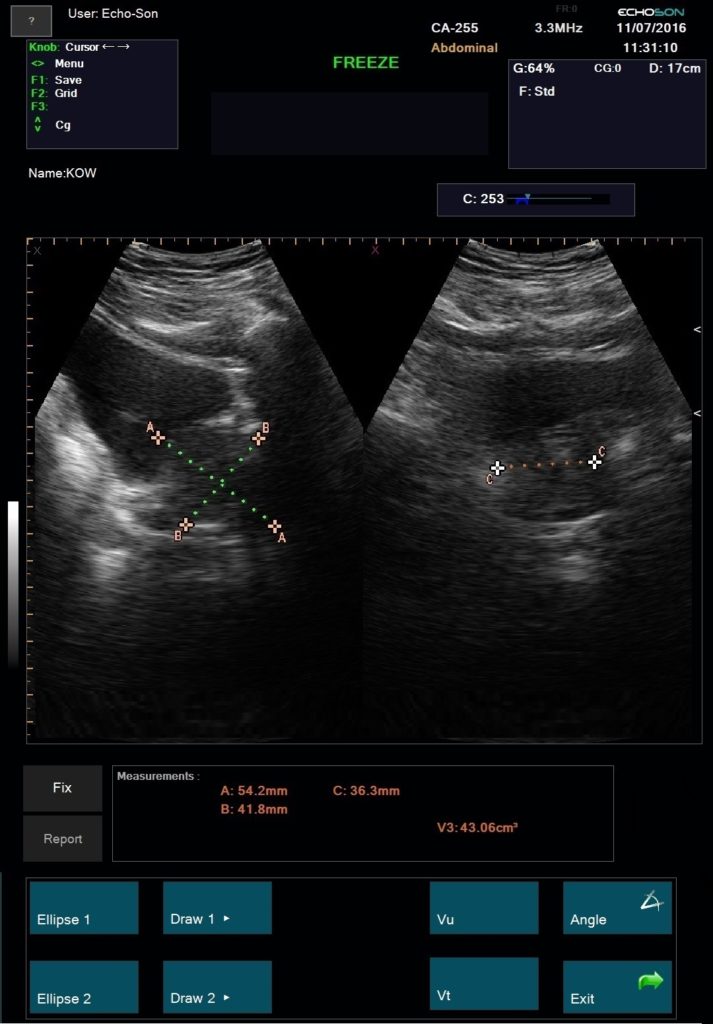
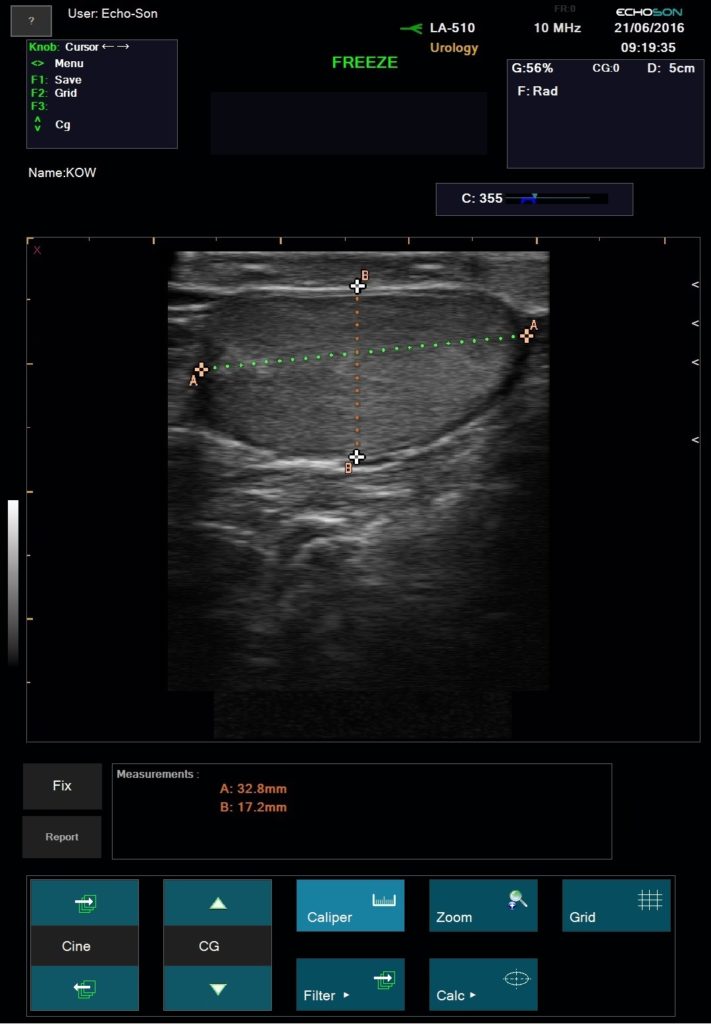
Measurements and calculations for the other applications – see parameters “ALBIT- General – Universal”

Frequency: 5,0 MHz- 17,0 MHz
Focus range: 9 – 60 mm
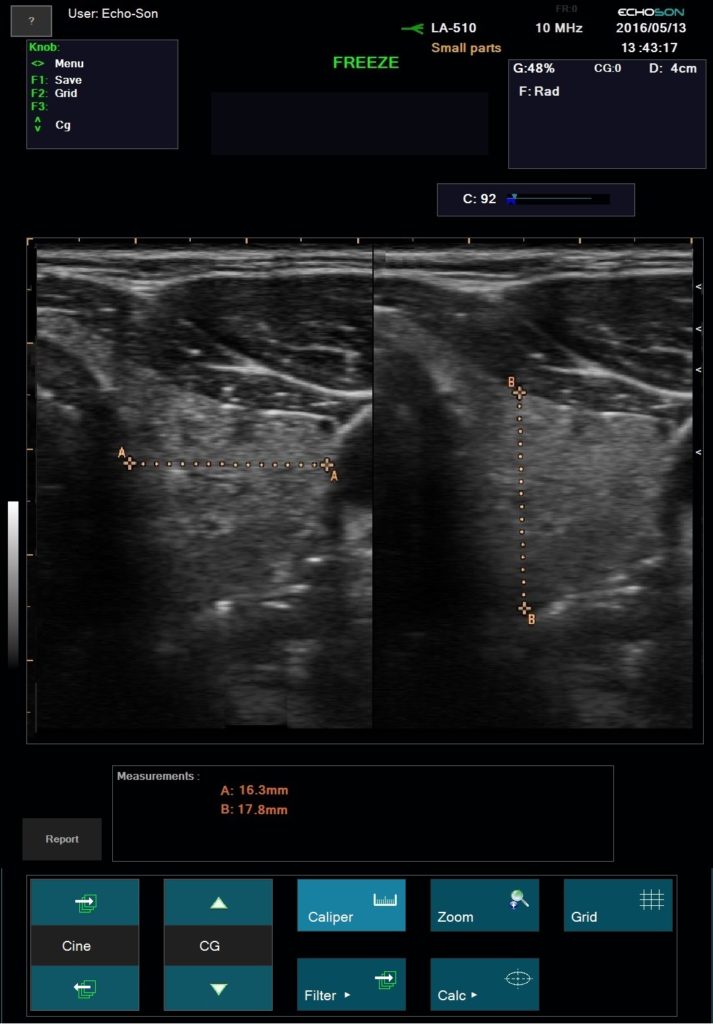
Application: organs and tissues superficially located, thyroid, breasts,scrotum, orthopedics, pediatric
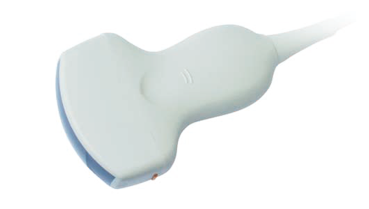
Frequency: multi-frequency 2,0 MHz – 5,0 MHz
Focus range: 20 – 160 mm
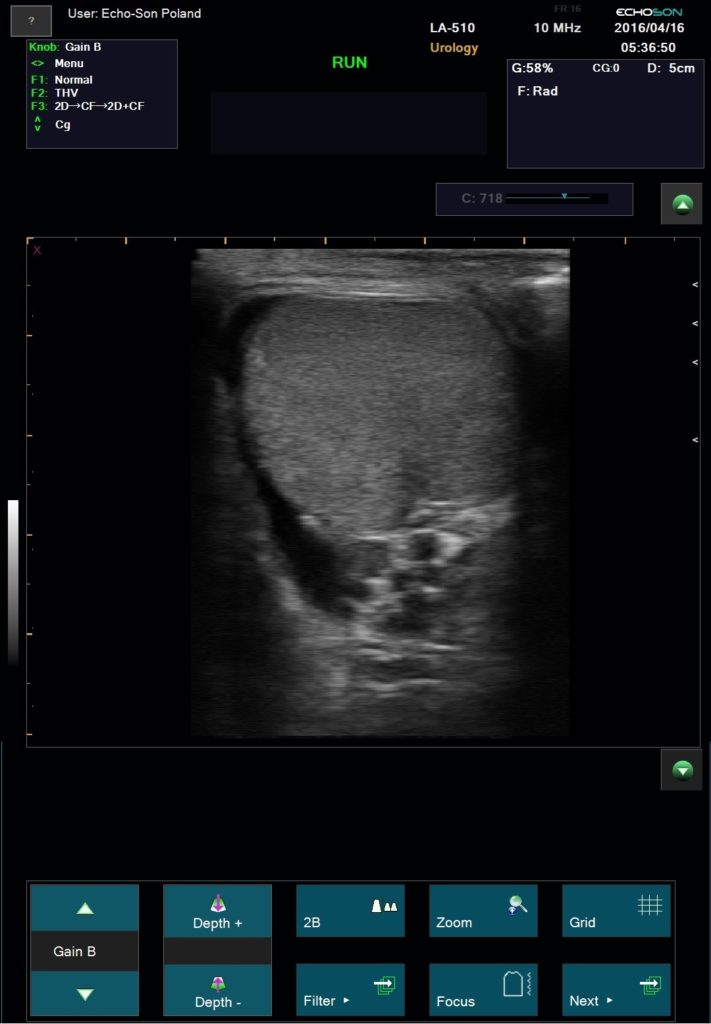
Application: abdomen, gynecology, obstetrics, F.A.S.T., urology